An in-depth review of Femoral Neck Fractures.
If you're interested in orthopedics you'll definitely want to check this review out.
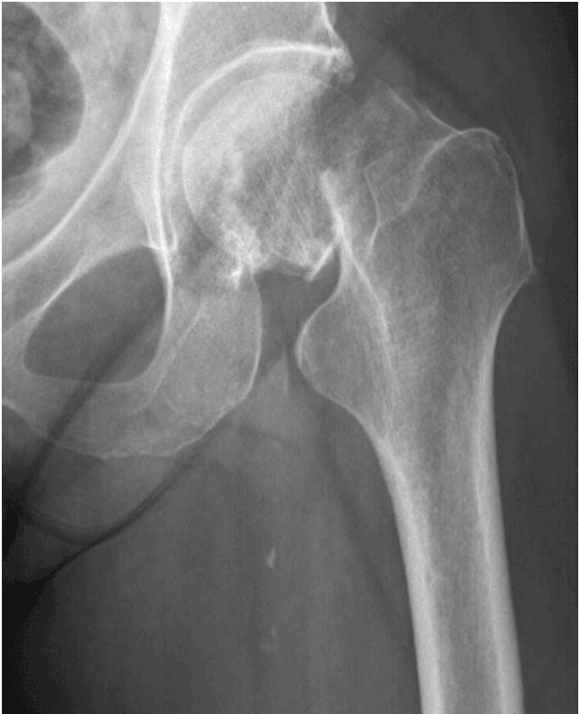
Femoral neck fractures have a reported one-year mortality rate as high as 33%.
Pre-injury mobility is the most important factor in determining post-op survival.
Chronic comorbidities increase one-year mortality rates, especially chronic renal failure.
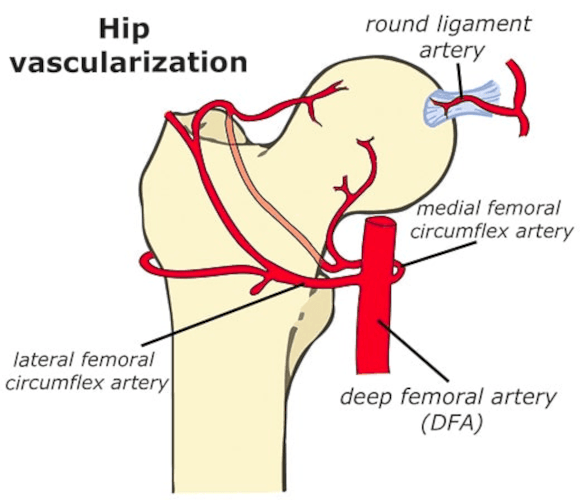
Femoral neck fractures can be divided into intracapsular and extracapsular. This is based on the blood supply to the region, the intracapsular region is supplied by the medial femoral circumflex artery and the blood supply may be disrupted in displaced fractures.
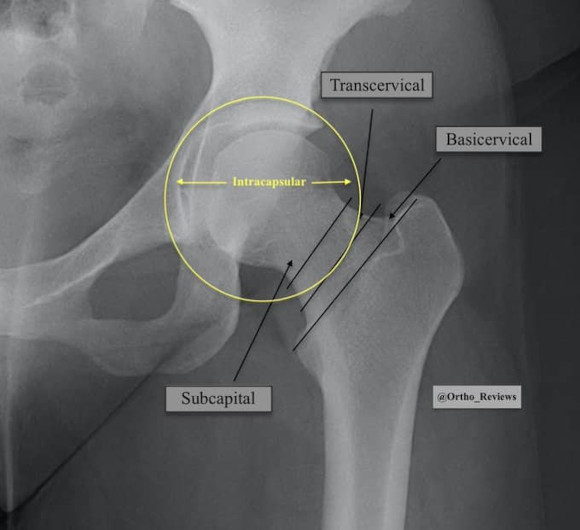
The femoral neck can be divided into three regions:
-Subcapital
-Transcervical
-Basicervical
The subcapital & transcervical regions are intracapsular and are treated the same.
The basicervical region is extracapsular and is treated like an intertrochanteric fx.
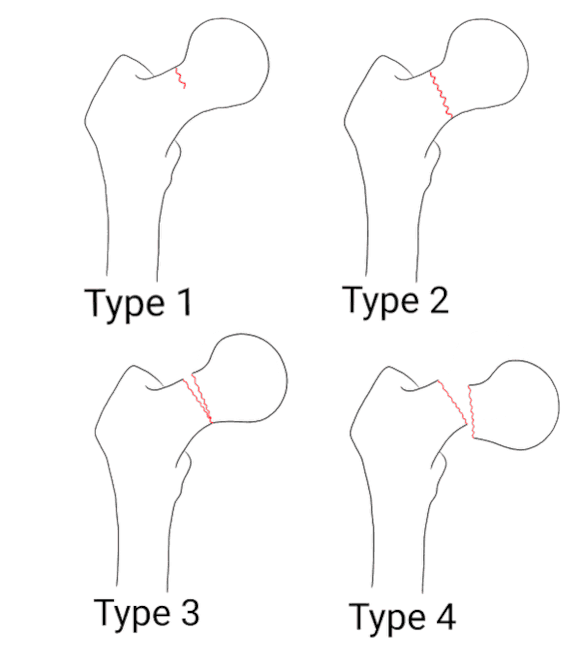
The Garden classification system is used to guide treatment. It is divided into four types:
Type 1: Incomplete – nondisplaced
Type 2: Complete – nondisplaced
Type 3: Complete- partially displaced
Type 4: Complete – fully displaced
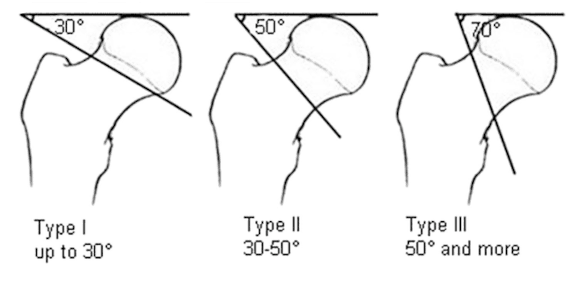
Pauwell’s classification is based on the angulation of the fracture, with higher degrees of angulation being associated with greater instability. It is divided into three types:
Type 1: 0-30 degrees
Type 2: 30-50 degrees
Type 3: > 50 degrees
Treatment depends on the displacement of the fx.
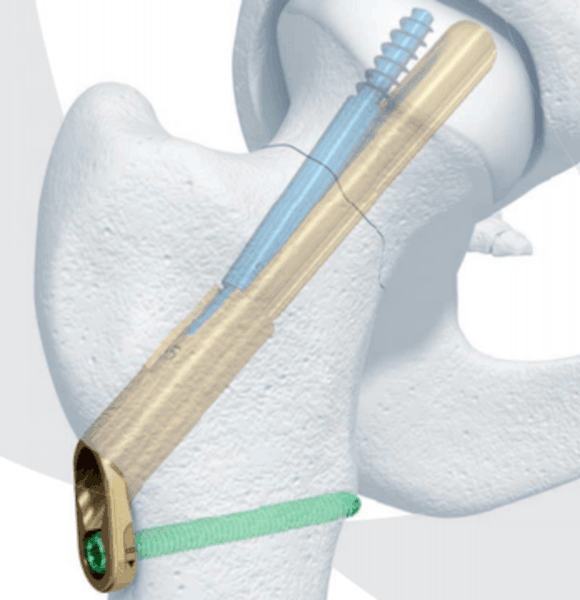
Non-displaced fractures (Garden 1/2) and displaced (Garden 3/4) fractures in young patients should be treated with ORIF.
ORIF options included cannulated screw fixation (left), femoral neck systems (right), & sliding hip screws
Treatment of displaced fractures (Garden 3/4) in elderly patients are treated by Hemi or Total Hip Arthroplasty.
The decision is based on the activity level and physiologic age of the patient.
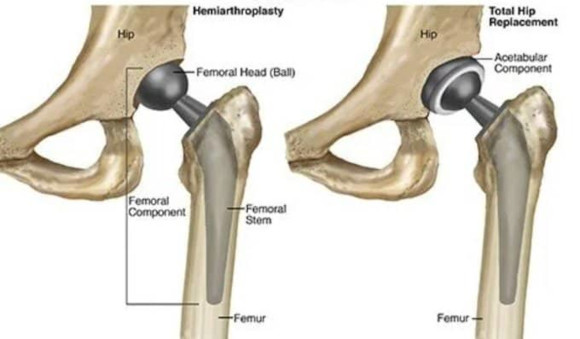
Total hip arthroplasties are associated with a greater risk of dislocation, longer surgical times, and greater blood loss.
For patients with lower activity levels and comorbidities that may prevent prolonged surgery, hemiarthroplasty may be a better choice.
For patients that are poor surgical candidates, a Girdlestone procedure may be utilized.
This procedure involves removing the femoral head and not replacing it. This procedure is reserved for debilitated patients and utilized for pain relief.
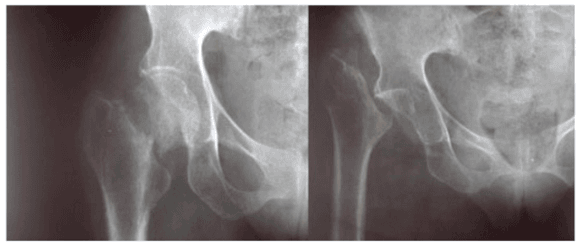
The most important complication to be aware of is osteonecrosis of the femoral head due to blood supply disruption.
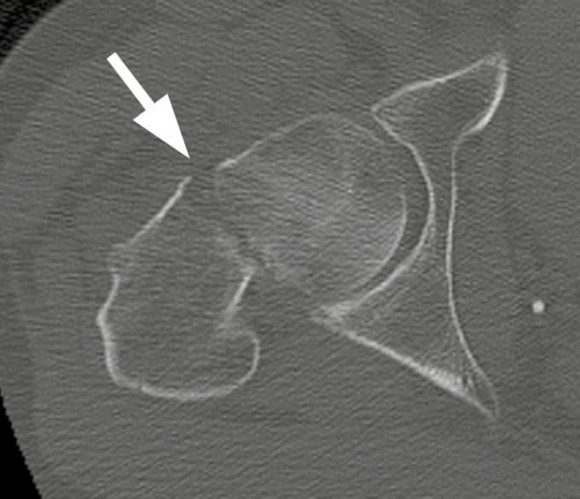
It may be beneficial to obtain a CT scan prior to choosing to treat suspected non-displaced fractures with ORIF.
 Full Review and Conversation on X
Full Review and Conversation on X